설명
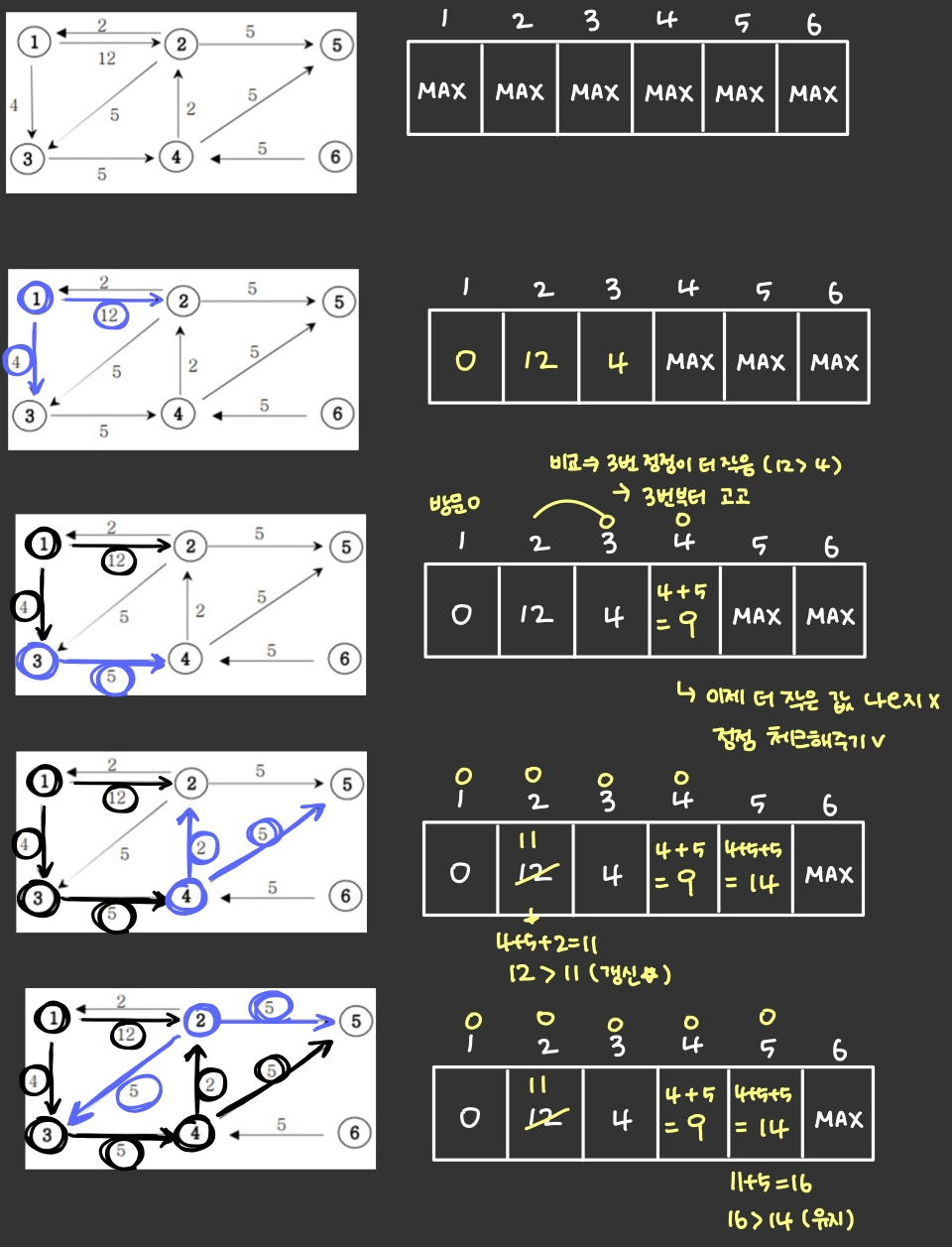
아래의 가중치 방향그래프에서 1번 정점에서 모든 정점으로의 최소 거리비용을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요. (경로가 없으면 impossible을 출력한다.)
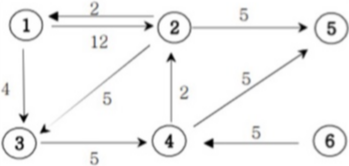
입력
첫째 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M가 주어진다. 그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결정보와 거리비용이 주어진다.
출력
1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소비용을 2번 정점부터 차례대로 출력하세요.
문제 해결
다익스트라 알고리즘
다익스트라 알고리즘은 다이나믹 프로그래밍을 활용한 대표적인 최단경로 탐색 알고리즘이다.
음의 가중치(음의 간선, 음의 값)가 없는 그래프의 한 노드에서 각 모든 노드까지의 최단거리를 구하는
알고리즘을 말한다.
다익스트라 알고리즘의 메커니즘은 기본적으로 아래 두 단계를 반복하여 임의의 노드에서 각 모든 노드까지의 최단거리를 구하는 문제에서 활용할 수 있다.
임의의 노드에서 다른 노드로 가는 값을 비용이라고 한다.
- 방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 가장 비용이 적은 노드를 선택 (그리디 알고리즘)
- 해당 노드로부터 갈 수 있는 노드들의 비용을 갱신 (다이나믹 프로그래밍)
가능한 적은 비용으로 가장 빠르게 해답에 도달하는 경로를 찾아내는 대부분의 문제에 응용된다!!
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int vex;
public int cost;
Edge(int vex, int cost) {
this.vex = vex;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge ob) {
return this.cost - ob.cost;
}
}- Edge 클래스는 그래프의 간선을 나타내며, 정점 번호인 vex와 비용 cost를 담고 있다.
- 우선순위 큐에 넣기 위해 Comparable 인터페이스를 구현해 비용을 기준으로 정렬한다.
- 이 떄 비용이 작은 것을 우선순위로 두었다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
P05_다익스트라알고리즘 T = new P05_다익스트라알고리즘();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
dis = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Edge(b, c));
}
T.solution(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= 2; i++) {
if (dis[i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.println(i + " : " + dis[i]);
else System.out.println(i + " : impossible");
}
}- 우선 모든 정점까지의 거리를 무한대로 초기화시켜준다
- 그리고 for문을 돌며 입력받아 그래프의 인접 리스트를 구성한다.
- 1번 정점에서 모든 정점으로 가는 최소 거리비용 구해야하므로 1에서 다익스트라 알고리즘을 수행한다.
<다익스트라 알고리즘>
public void solution(int v) {
PriorityQueue<Edge> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>();
pQ.offer(new Edge(v, 0));
dis[v] = 0;
while (!pQ.isEmpty()) {
Edge tmp = pQ.poll();
int now = tmp.vex;
int nowCost = tmp.cost;
if (nowCost > dis[now]) continue;
for (Edge ob : graph.get(now)) {
if (dis[ob.vex] > nowCost + ob.cost) {
dis[ob.vex] = nowCost + ob.cost;
pQ.offer(new Edge(ob.vex, nowCost + ob.cost));
}
}
}
}- 우선순위큐 pQ를 선언해 현재 거리가 가장 짧은 정점을 우선적으로 처리하도록 한다.
- pQ.offer(new Edge(v, 0)): 시작점을 비용 0으로 큐에 추가
- dis[v] = 0: 시작점의 거리를 0으로 설정
- 큐가 비어있지 않는 동안, 가장 비용이 적은 정점을 꺼내어 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 거리를 갱신해간다.
- if (nowCost > dis[now]) continue;: 이미 처리된 정점이면 continue
- if (dis[ob.vex] > nowCost + ob.cost): 현재 정점을 거쳐서 가는 것이 더 짧은 경우 거리를 갱신하고, 해당 정점을 우선순위 큐에 추가
최종 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P05_다익스트라알고리즘 {
static int n, m;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> graph;
static int[] dis;
public void solution(int v) {
PriorityQueue<Edge> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>();
pQ.offer(new Edge(v, 0));
dis[v] = 0;
while (!pQ.isEmpty()) {
Edge tmp = pQ.poll();
int now = tmp.vex;
int nowCost = tmp.cost;
if (nowCost > dis[now]) continue;
for (Edge ob : graph.get(now)) {
if (dis[ob.vex] > nowCost + ob.cost) {
dis[ob.vex] = nowCost + ob.cost;
pQ.offer(new Edge(ob.vex, nowCost + ob.cost));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
P05_다익스트라알고리즘 T = new P05_다익스트라알고리즘();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
dis = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Edge(b, c));
}
T.solution(1);
for (int i = 2; i <= 2; i++) {
if (dis[i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.println(i + " : " + dis[i]);
else System.out.println(i + " : impossible");
}
}
}
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int vex;
public int cost;
Edge(int vex, int cost) {
this.vex = vex;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge ob) {
return this.cost - ob.cost;
}
}반응형